UVC Overview
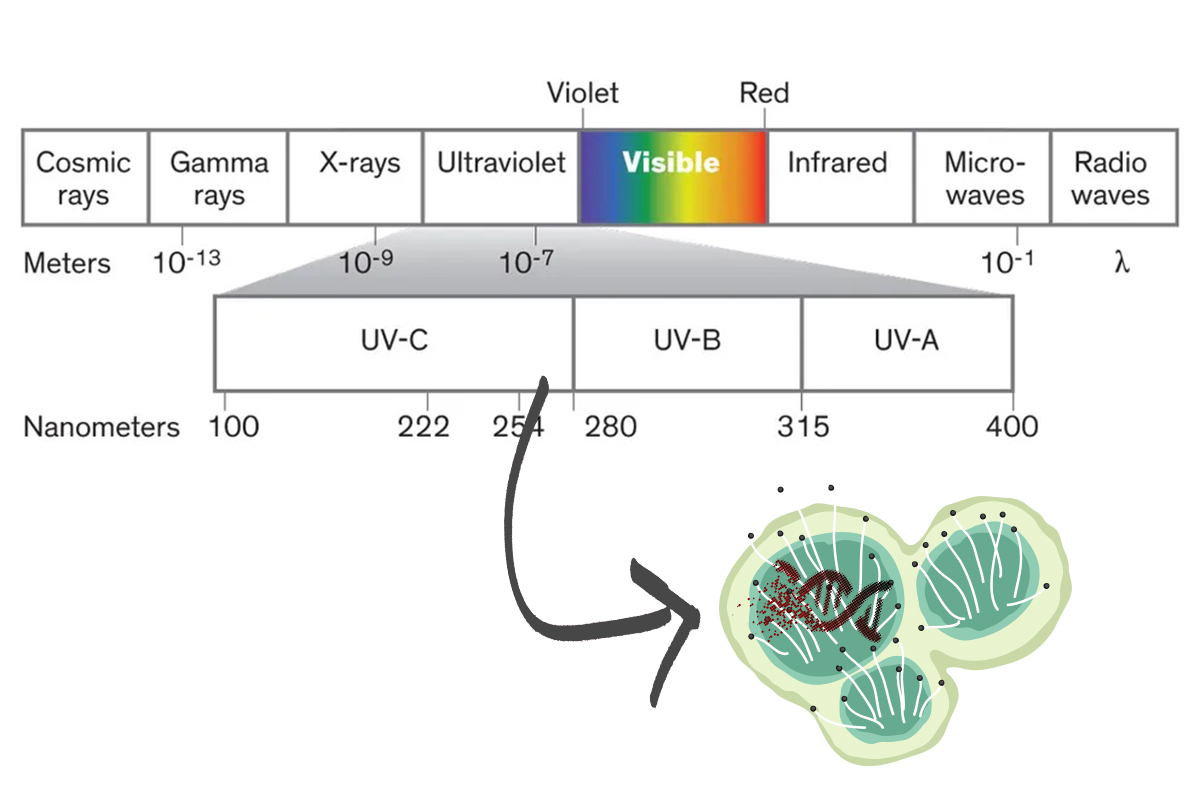
Ultraviolet light is composed of three wavelength ranges.
- UVC, from 100 nanometers (nm) to 280 nm.
- UVB, from 280 nm to 315 nm.
- UVA, from 315 nm to 400 nm.
UV wavelength corresponds directly to the amount of time needed for effective exposure. The shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency and greater the power. Greater power means the exposure time required to kill microorganisms is less. UVC at longer wavelengths and lower frequency/lower power is safer for the user, but a longer continuous exposure time is needed to kill microorganisms.
UVC’s germicidal eradication efficiency reaches peak activity around 265 nm. All wavelengths of UVC light will penetrate and damage the DNA and RNA structures of microorganisms. But UVC does so most effectively and in the shortest amount of time at the 265 nm wavelength (1).
UVC Technology
LEDs and lamps are the two options available for UVC disinfection. It is important to consider several factors when comparing the two.
Estimated Power Output
An advantage LEDs have is that they provide a specific light output, such as the optimal 265 nm. Whereas a lamp is limited to 254 nm.
Application Requirements
LEDs can be arranged in a way to cover more specific areas and with greater intensity. This allows UVCs to make better use of UVC power with their focused directional output.
Lamps typically require a warm-up time before they reach full output power. Likewise, turning lamps on and off again greatly reduces their overall lifespan. As a lamp ages, more and more voltage is needed to produce the same amount of light until the lamp fails. This is why they become less and less efficient over time.
Lamp Pros
- Been around for more than 100 years
- Generally viewed as an efficient way to provide lighting over a vast area as they are more efficient and last longer than incandescent bulbs (however they fail in both regards when compared to LED).
Lamp Cons
- Contain toxic mercury or xenon, hazardous materials that are a waste disposal issue. The toxic gases can be released if the bulb (which is often openly exposed) is broken, putting personnel at risk.
- They age significantly if frequently switched on and off. Typical lamp life ranges from 7,000 to 15,000 hours but degrades rapidly with turning the lamp on and off.
- Lights are omnidirectional. This means it produces 360 degrees of light. This is a major inefficiency because at least half the light requires reflection in an attempt to reach the desired surface.
LED Pros
- Extremely long lifespan, lasting 20,000 to 200,000 hours or more depending on the technology.
- Extremely energy efficient. This is because they waste little energy in infrared radiation and emit light directionally.
- Very high light quality and consistent intensity.
- Very low maintenance costs and hassle (do not require bulb replacement for the life of product).
- Can have variety in their form, allowing for smaller, more usable designs.
- Have faster switching. No warm-up or cool-down periods to accommodate.
LED Cons
- Tend to have a higher up-front cost.
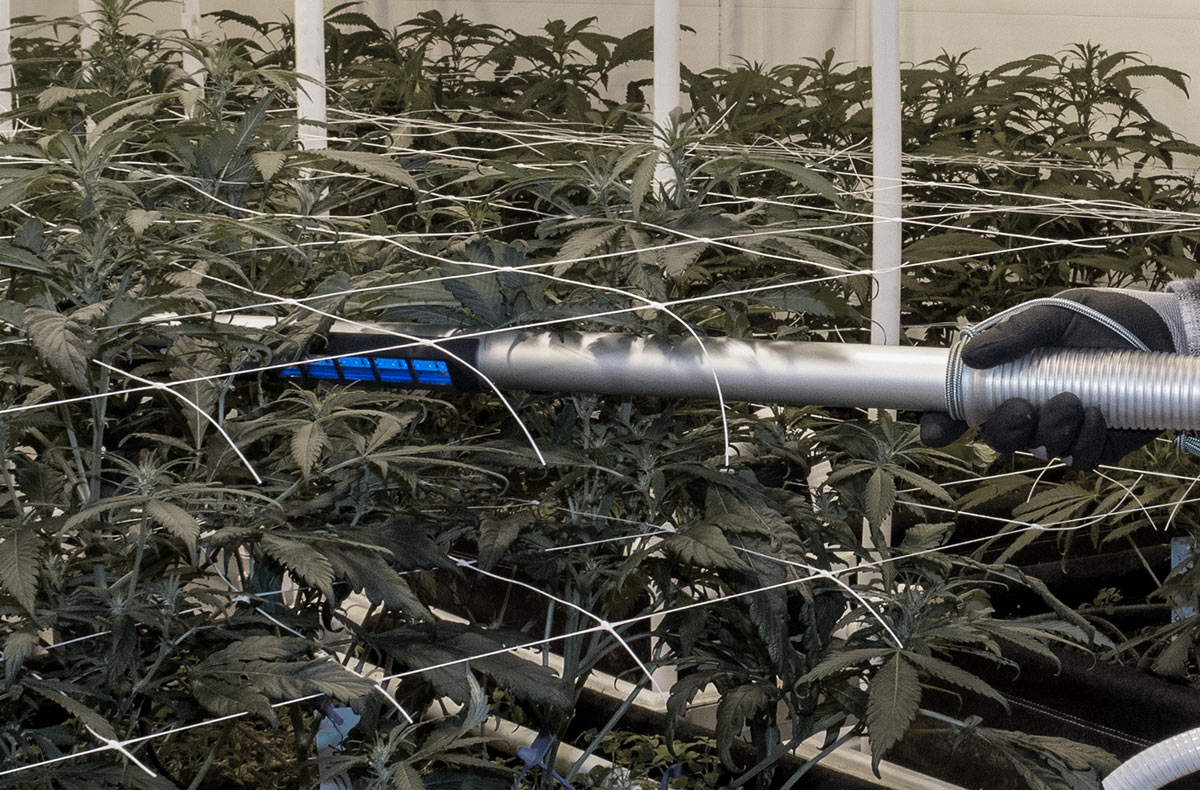
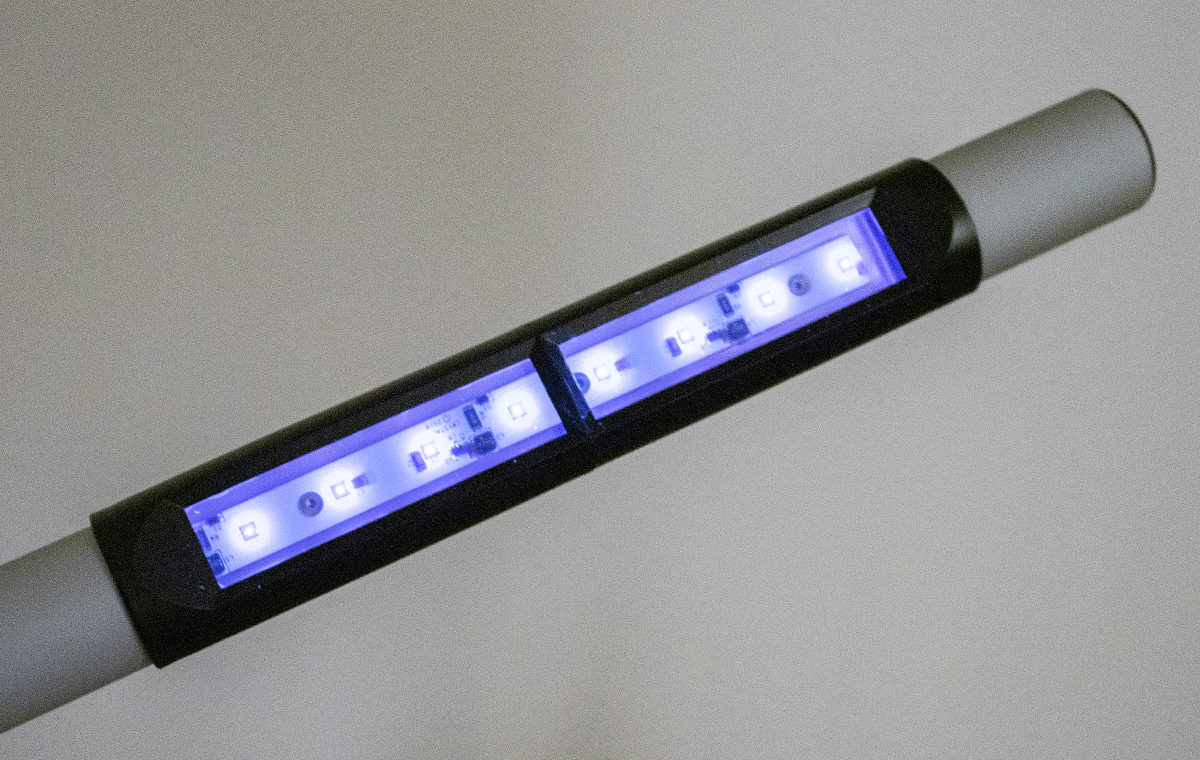
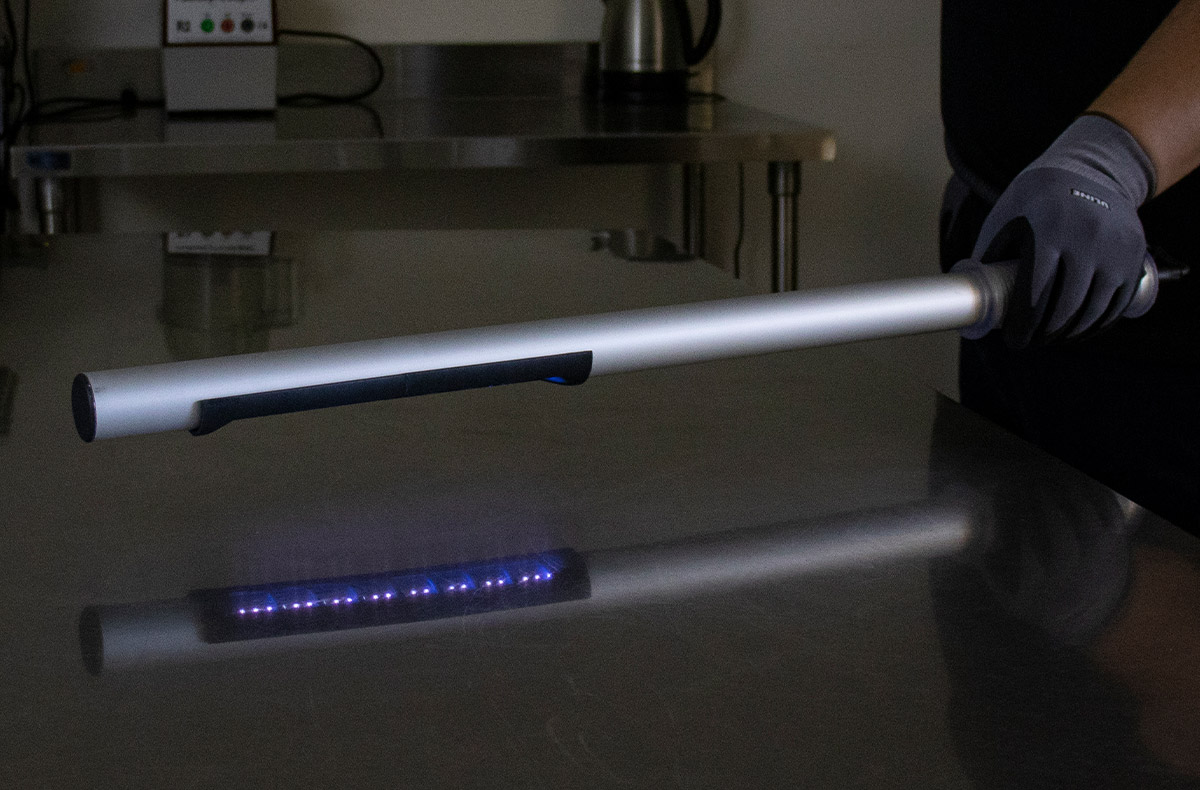
Unique features of the Element Grow Katana not seen in competitor LED products:
- Waterproof, allowing for safe use in a variety of environments as well as the ability to efficiently sanitize the unit.
- Truly portable (uses battery pack, not outlet)
- Ergonomic, ultra slim design combats user fatigue and reaches hard to access places.
- Lightweight, only 21.5 oz/0.61 kg.
Technology Comparison Chart
*Foot candle is a measure that describes the amount of light reaching a specific surface area as opposed to the total amount of light being emitted from a source.
** System efficiency is the measure of light that actually reaches the target area after all losses are accounted for (lumens/watts).
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4702654/